Corporate Governance
Corporate Governance Structure
Toyota Industries strives to enhance its corporate value in a stable manner over the long term and maintains society's trust by earnestly fulfilling its social responsibilities in accordance with its Basic Philosophy. To that end, Toyota Industries endeavors to further enhance its corporate governance in its efforts to maintain and improve management efficiency and the fairness and transparency of its corporate activities.
Basic Perspective on Corporate Governance
Toyota Industries regards the most important managerial task is to earn trust broadly from society and enhance our corporate value on a stable, long-term basis. We aim to do this task based on our Basic Philosophy and by earnestly fulfilling our social responsibilities. Our basic focus is on contributing to the creation of an enriched society through business activities, and we believe it is essential to cultivate good relationships with stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, business partners, creditors, local communities and employees.
Accordingly, we strive to enhance our corporate governance in order to maintain and improve management efficiency, fairness and transparency. For example, we have established a structure to quickly and flexibly respond to changes in the business environment and have been working to augment management oversight and ensure the timely disclosure of information.
More specifically, the following basic policies drive our initiatives.
- (1) We seek to ensure shareholders’ rights and equality.
- (2) We seek to promote appropriate collaboration with stakeholders other than shareholders (including customers, business partners, creditors, local communities and employees).
- (3) We seek to conduct appropriate information disclosure and ensure transparency.
- (4) We seek to perform the roles and duties of the Board of Directors appropriately in order to make decisions in a transparent, fair, quick and resolute manner.
- (5) We seek to promote a constructive dialogue with shareholders.
Implementation Structure
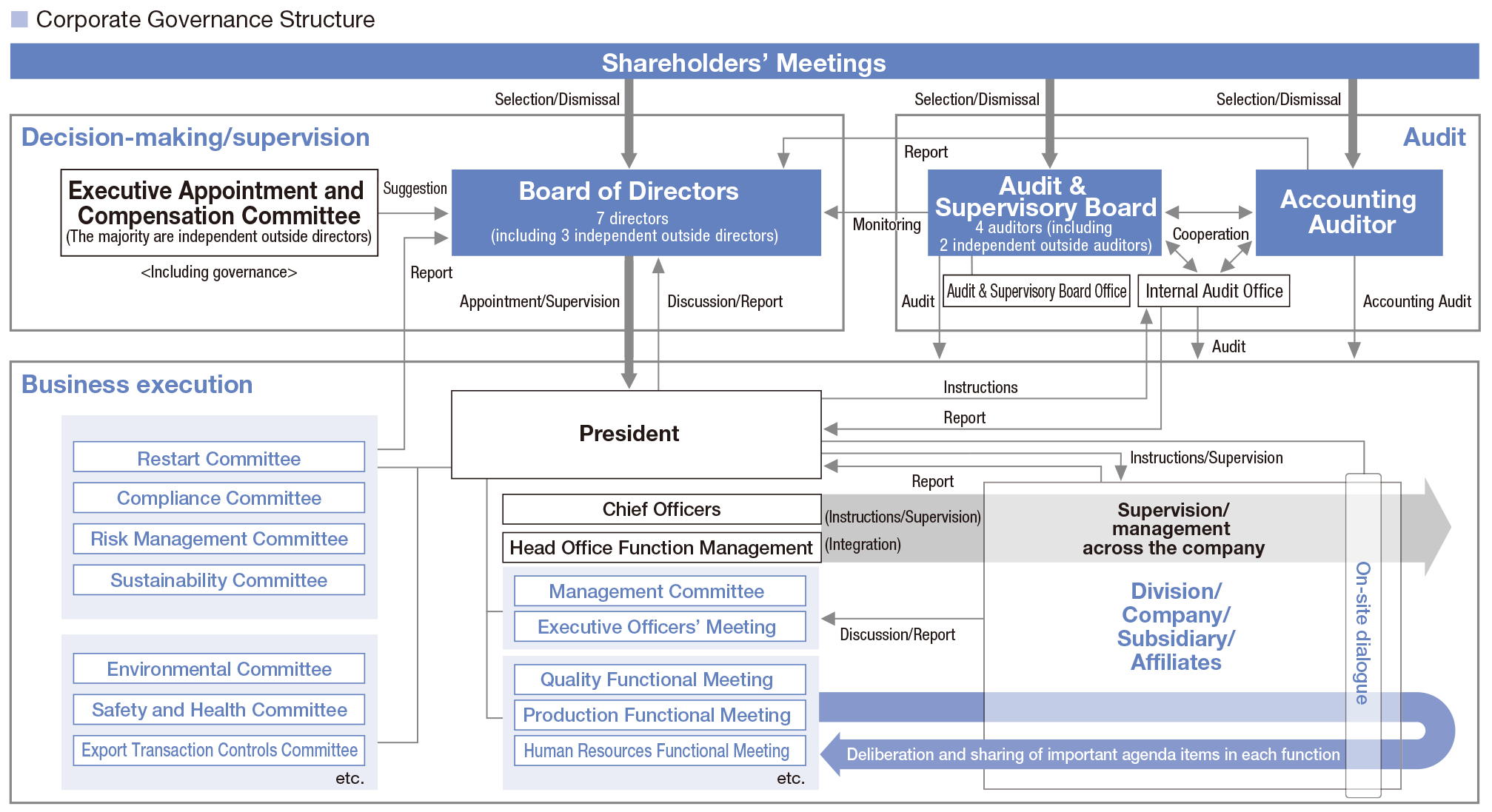
Toyota Industries convenes monthly meetings of the Board of Directors to resolve important management matters and monitor the execution of duties by directors. We appoint outside directors who have a wealth of experience and knowledge such as business management. They attend meetings of the Board of Directors and give opinions and ask questions as deemed necessary based on their individual, wide-ranging experience and insights related to the management of globally operating companies and monozukuri (manufacturing). Through this supervisory function of outside directors, we ensure the legality and validity of the Board's decisions as well as the directors' execution of duties from an objective perspective. Moreover, a variety of issues concerning important management matters, such as our corporate vision, management policies, medium-term business strategies and major investments, as well as crucial projects in each business division, are discussed by the Management Committee, which is composed of the president, chief officers and audit & supervisory board members as well as relevant senior executive officers and other executives, prior to deliberation by the Board of Directors.
At the Executive Officers' Meeting, the president, chief officers and senior executive officers convene to report and confirm the monthly status of business operations and discuss business and functional issues.
In addition, issues pertaining to quality, production and human resources are discussed at the corresponding functional meetings. We have also put in place committees to deliberate on more specific matters, such as compliance, risk management, sustainability, the environment, safety and health as well as export transaction controls. These functional meetings and committees discuss important matters and action themes in respective areas.
Furthermore, in response to the engine certification issue, we established a Restart Committee to promote recurrence prevention measures.
Moreover, we strive to maintain and improve internal controls by establishing the Internal Audit Office and conducting internal audits of Toyota Industries' business divisions and departments as well as our subsidiaries.
Selection and Dismissal of Senior Management and Appointment of Director and Audit & Supervisory Board Member Candidates
Policies and Procedures for Selection (and Dismissal) of Senior Management and Appointment of Director and Audit & Supervisory Board Member Candidates
We appoint candidates from the viewpoint of placing the right persons in the right positions. As director candidates, we appoint persons capable of making sound and quick decisions about corporate management in general, managing risk appropriately and monitoring the execution of business operations. In appointing audit & supervisory board member candidates, we ensure a balance among the financial, accounting and legal insights, knowledge of our business fields and the diversity of perspectives on corporate management. We also select senior management members from the viewpoint of placing the right persons in the right positions, while considering a balance of their abilities to cover each function and business division of Toyota Industries in executing business operations. We will consider dismissal if a certain situation precludes sufficient execution of duties.
Based on these policies, we review proposals, exchange views and confirm details at the Executive Appointment and Compensation Committee, which is chaired by an independent outside director and a majority of which comprising independent outside directors, and then submit these proposals to the Board of Directors for resolution.
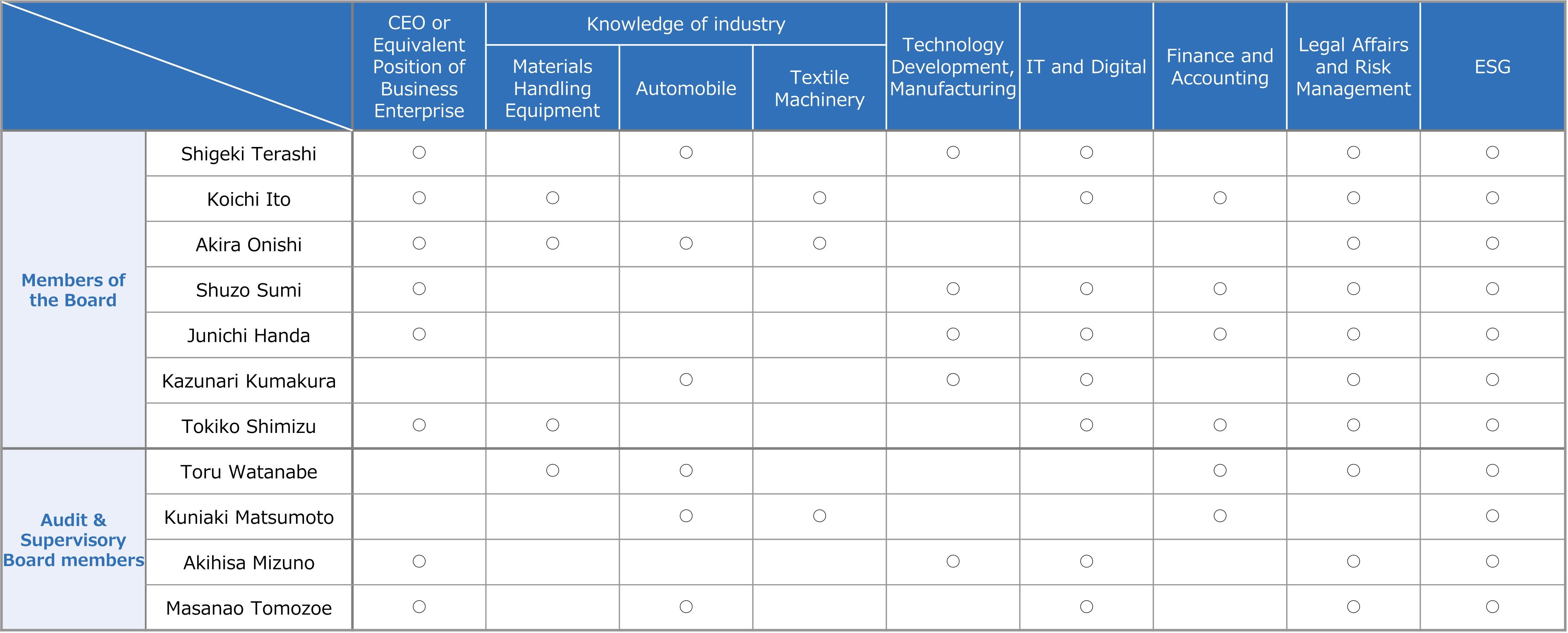
■Experience and Expertise of Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board Members
Appointment of Independent Members of Management
As a publicly listed company, Toyota Industries strives to ensure the fairness and transparency of management. Following the Securities Listing Regulations stipulated by the Tokyo Stock Exchange and Nagoya Stock Exchange, respectively, to further enhance our corporate governance, Toyota Industries has appointed as independent members of management three outside directors and two outside audit & supervisory board members who are deemed to have no conflicts of interest with our shareholders.
Determination of Compensation for Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board Members
Matters Related to Policy for Determining Individual Compensation for Directors
- ■Basic Perspective
-
・We ensure fairness and transparency.
・We emphasize incentives for achieving better business performance and sustainable growth, link compensation with the business performance of Toyota Industries and reflect individual duties and performance.
- ■Compensation Structure
-
・Compensation for directors consists of fixed compensation (basic compensation) and performance-linked compensation (bonuses and restricted share compensation).
・However, non-executive directors such as outside directors are paid only fixed compensation as they are independent of the execution of business operations.
- ■Method of Determining Individual Compensation
-
・We have established the Executive Appointment and Compensation Committee consisting of Toyota Industries' president and independent outside directors.
・To ensure the Committee's objectivity and transparency, we have a rule that independent outside directors serve as a chairman and make up half or more of the total number of its members.
・The Executive Appointment and Compensation Committee deliberates on a policy for determining individual compensation for directors, proposed compensation for each director and important matters related to compensation.
・The Board of Directors votes on the policy based on the results of deliberations made at the Executive Appointment and Compensation Committee.
・From the standpoint of determining directors' individual compensation amounts flexibly and swiftly, the Board of Directors delegates the related decision-making authority to the president.
・The president determines the directors' individual compensation amounts based on the policy and the results of deliberations made at the Executive Appointment and Compensation Committee.
- ■Composition Ratio
-
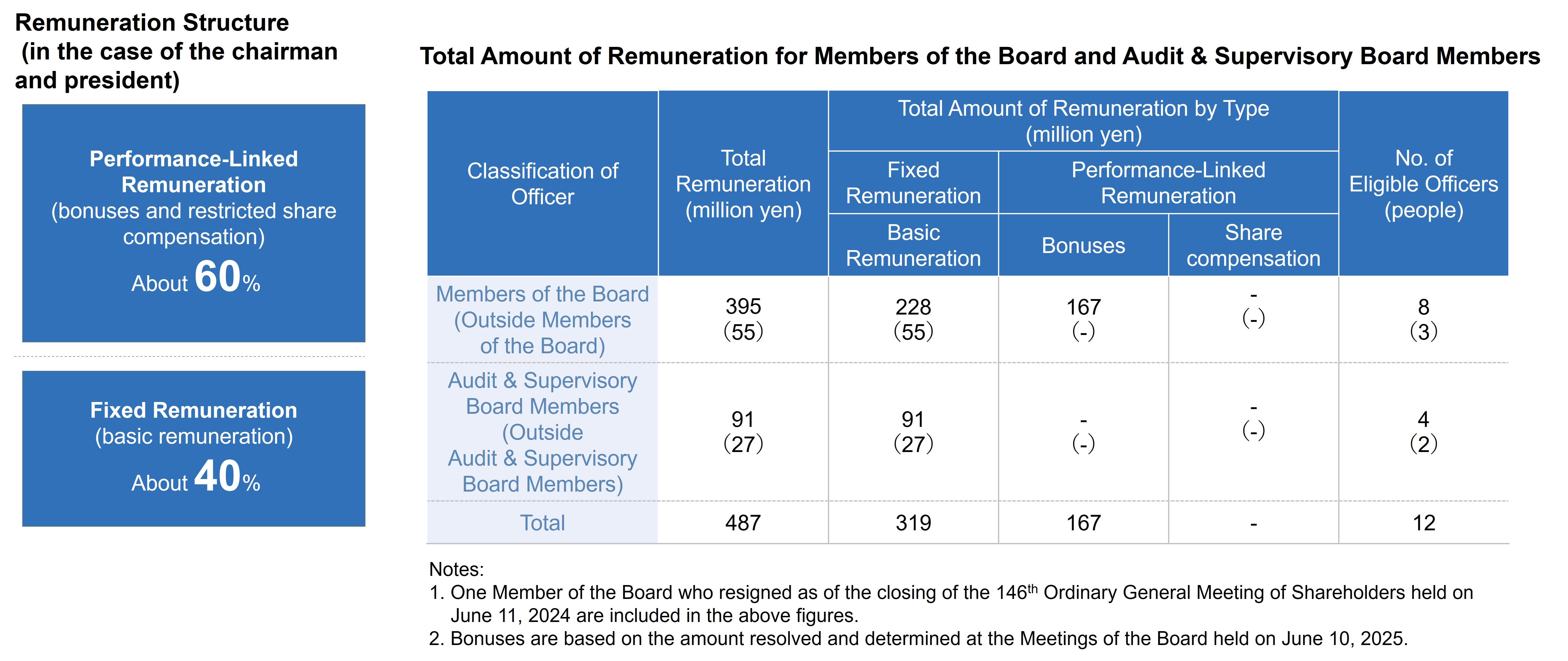
・The ratio of fixed compensation and performance-linked compensation (bonuses and restricted share compensation) for directors, excluding non-executive directors such as outside directors, is approximately 40:60 (in the case of the president and the chairman). However, Toyota Industries is not precluded from using a ratio different from the above, depending on the circumstances of the consolidated operating profit amount and others.
・The ratio of bonuses to restricted share compensation in the performance-linked compensation is approximately 70:30.
- Policy for Determining Fixed Compensation, Bonuses (together, “Cash Compensation”) and Restricted Share Compensation
- [Cash Compensation]
The cash compensation paid to directors after combining fixed compensation and bonuses is determined to be ¥700 million or less per year (including ¥150 million or less per year for outside directors). - [Fixed Compensation]
・Fixed compensation for directors consists of monthly salaries, which are paid periodically while in service.
・We determine a reasonable level of individual compensation amounts while giving consideration to other companies' compensation levels as well as the rank and duties of each director.
[Bonuses]
・We pay a bonus at a certain time after the end of the General Shareholders' Meeting in each fiscal year.
・The bonus is determined by using the consolidated operating profit as the indicator and is approximately 70% of the total amount of performance-linked compensation calculated for each rank based on the amount of consolidated operating profit for the previous fiscal year. The bonus will be 100% of the total amount of performance-linked compensation if there is a reason for not providing directors with restricted share compensation.
・In determining the total amount of performance-linked compensation, we give comprehensive consideration to dividends, employees' and other companies' bonus levels, past records of bonus payments and execution of duties and assigned work.
[Restricted Share Compensation]
・Restricted share compensation is paid at a certain time after the end of the General Shareholders' Meeting in each fiscal year. If there is a reason for not providing directors with restricted share compensation, all of their performance-linked compensation is paid as a bonus and restricted share compensation is not paid.
・Compensation paid to provide restricted share units is a pecuniary claim, and the total amount is ¥200 million or less per year separate from the director's fixed compensation and bonus. The class of shares allotted is common share (with a transfer restriction attached to the allotment contract), which is issued or transferred, and the total number is 60,000 shares or less per year (if the total number of Toyota Industries' outstanding shares has changed due to a share split or reverse share split, including the allotment of shares without contribution, the ceiling amount is adjusted according to the ratio), as per the resolution approved at the 146th Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders.
・The restricted share compensation is determined by using the consolidated operating profit as the indicator and is approximately 30% of the total amount of performance-linked compensation calculated for each rank based on the amount of consolidated operating profit for the previous fiscal year.
・Restricted share compensation is provided on the condition that an allotment contract, which includes the following provisions, is concluded.
■A transfer restriction is attached to the shares allotted for a period between three years and 30 years from the date of allotment, which is determined in advance by the Board of Directors, and the restriction will be lifted at the expiration of the period. The transfer restriction will be lifted if a director has retired from their position due to the expiration of their term of office, death or other legitimate reasons.
■If a director violates a law or any of the events specified by the Board of Directors occurs during the period of transfer restriction, Toyota Industries may acquire all or part of the shares allotted for no consideration.
Compensation for Audit & Supervisory Board Members
Compensation for audit & supervisory board members is fixed remuneration only, and is determined through discussions among audit & supervisory board members in accordance with certain standards established by Toyota Industries.
Efforts for Undertaking Management Conscious of Capital Cost and Stock Prices
To enhance our corporate value over the medium to long term, Toyota Industries focuses on management conscious of capital cost while working to provide products and services that anticipate market needs and benefit society.
Specifically, we aim for a return on equity (ROE) of 6% in around 2026 or 2027. In the medium to long term, we will seek an even higher ROE and greater corporate value with a focus on increasing profitability, reducing shareholders' equity by trimming stock holdings, which include cross-shareholdings, and investing in infrastructure. Other key efforts are growth-oriented research and development, proactive M&A investment, shareholder returns through dividends and flexible share buyback and dialogue with the market. Please refer to the following for details.
Note: As stated in the Company's announcement titled "Notice Concerning Expression of Opinion in Support of Planned Commencement of Tender Offer for Company Shares by Toyota Fudosan Co., Ltd. and Neutral Opinion to Tender Share Therein", dated June 3, 2025, a tender offer for the Company's common shares is scheduled to commence by a corporation to be established by Toyota Fudosan Co., Ltd.
According to Toyota Fudosan Co., Ltd., the purchase price for the tender offer was determined on a comprehensive basis, based on the assumption that interim dividends based on the record date of September 30, 2025 and year-end dividends based on the record date of March 31, 2026 would not be paid. Accordingly, the Company passed a resolution at its Board of Directors meeting to amend the dividend forecast for the fiscal year ending March 2026 and not to pay any interim or year-end dividends for the fiscal year ending March 2026.
FY2025 4Q Financial Results IR Conference presentation
FY2025 2Q Financial Results IR Conference presentation
FY2024 4Q Financial Results IR Conference presentation
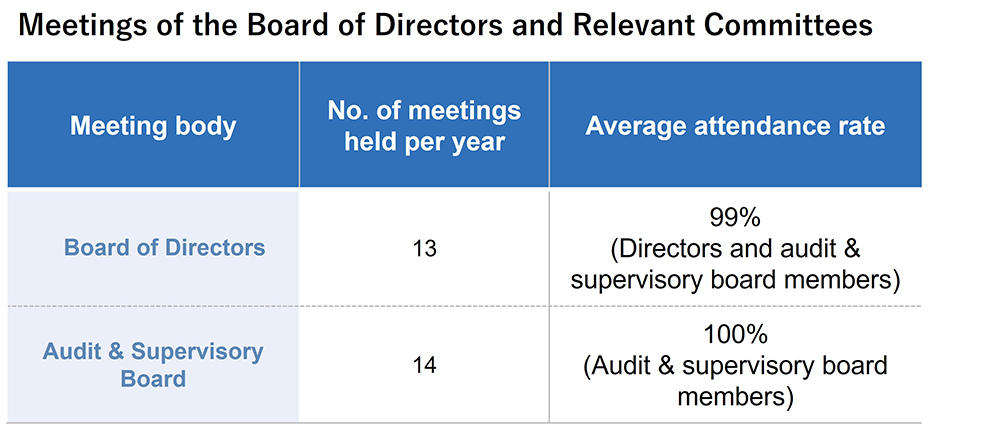
Effectiveness of the Board of Directors and Its Evaluation
With regard to the effectiveness of the Board of Directors, the Company conducts questionnaire surveys and interviews mainly with outside directors and audit & supervisory board members and holds discussions with them to increase effectiveness. The following summarizes the results of their evaluation.
- ■Evaluation
-
1) The Board of Directors is recognized as fostering an atmosphere where opinions can be expressed openly, facilitating constructive discussions and active exchanges of ideas. Additionally, it is deemed to possess a framework and functionality that are both necessary and sufficient for its operations.
2) Apart from the Board meetings, there is a separate space for informal discussions involving business division executives, enabling access to a wide range of information. These discussions serve as valuable opportunities to deliberate on the overall direction of management.
- ■Feedback for Further Improvement of the Effectiveness
-
1) It would be beneficial to employ additional measures that make it easier to grasp on-the-ground and operational challenges, especially in the context of reporting on business execution.
2) At the initial stages of reviewing mid- to long-term plans, increasing opportunities for in-depth discussions on growth strategies with business division executives is recommended.
As shown above, Toyota Industries' Board of Directors has been evaluated as effective. Nonetheless, we will undertake efforts to further increase the effectiveness on a continuous basis.
Audit & Supervisory Board Members and Audit & Supervisory Board
Toyota Industries has four audit & supervisory board members, two of whom are full-time members and two of whom are outside members.
The four members attend meetings of the Board of Directors and provide their opinions as appropriate. The full-time members also attend other important meetings and receive reports on the execution of duties by directors and other responsible persons. They work to monitor and provide advice on the management status through on-site audits at the Head Office, major business sites and subsidiaries, thereby contributing to the maintenance and improvement of internal controls. They also collaborate appropriately with the accounting auditor and the Internal Audit Office.
Meetings of the Audit & Supervisory Board are held every month to share information on audits conducted by full-time members with outside members, to receive reports on important business statuses from Board members and responsible persons, and to receive reports from the accounting auditor regarding how key audit matters have been examined and determined.
At these meetings, the members also discuss and make decisions on important matters, such as audit policies and plans, the audit method used by the accounting auditor and the appropriateness of their audit results.
Corporate Governance Report
 Corporate Governance Report(Last Update: November 11, 2025) PDF [615.1KB / 21pages]
Corporate Governance Report(Last Update: November 11, 2025) PDF [615.1KB / 21pages]
| Initiatives for Enhancing Corporate Governance |
|---|
|
Cross-Shareholdings
Policy on Cross-Shareholdings
Toyota Industries' basic policy is not to own cross-shareholdings unless there is a rational reason to do so. On the other hand, collaboration, such as maintaining and reinforcing business relationships with business partners, is essential to sustainably enhance our corporate value. We thus hold shares as needed based on our business strategies.
Verifying Appropriateness of Cross-Shareholdings
Each year, the Board of Directors verifies if the purpose of cross-shareholdings is appropriate and if associated benefits and risks are commensurate with capital cost.
More specifically, we annually conduct a survey on the significance of cross-shareholdings with responsible departments to pick out less significant investee companies and examine whether to sell their shares. At the same time, we carry out verification based on quantitative information, such as profitability indicators of investee companies and investment returns compared to capital cost. If those investee companies are found to be below our criteria as a result of the verification, we again examine the significance of holding their shares and consider selling these shares.
In fiscal 2025, we sold shares of six investee companies.
Exercise of Voting Rights
1) While respecting the management policies of individual investee companies, the Company determines how to exercise its voting rights by checking each item on the agenda from the perspectives of medium- to long-term enhancement of corporate value, policy concerning shareholder returns, corporate governance and social responsibility.
2) Key Proposals Subject to Assessment
(1) Expansion of authorized capital
(2) Anti-takeover measures
(3) Business reorganization and related matters
(4) Shareholder returns
(5) Appointment and dismissal of directors
Internal Control System
In accordance with the Companies Act, in May 2006 Toyota Industries' Board of Directors adopted the Basic Policies for the Establishment of an Internal Control System (Basic Policies) to ensure compliance, risk management as well as the effectiveness and efficiency of business operations by incorporating these policies into each business segment's annual policies and day-to-day routine management. However, following our legal violations related to engine certification in Japan, we initiated efforts to prevent recurrence while going back to the basics and making a fresh start, vowing never to commit such misconduct again. At the same time, we decided to revise our Basic Policies, and the decision was approved by resolution of the Board of Directors in April 2024.
In order to never repeat the same mistake, we will foster a culture of noticing and always pausing when something is wrong and make improvements by engaging all employees. We will also establish an organization and system to respond to risk appropriately and make optimum allocation of management resources. In executing actual business operations, we will remain sincere and conduct proper manufacturing, incorporate a mechanism, including a check function, into our corresponding processes, and simultaneously work to nurture human resources to practice such sincere, proper manufacturing.
We assess the implementation status at the end of each fiscal year and determine actions for the coming year, including reviewing the implementation structure and enhancing day-to-day operational management.
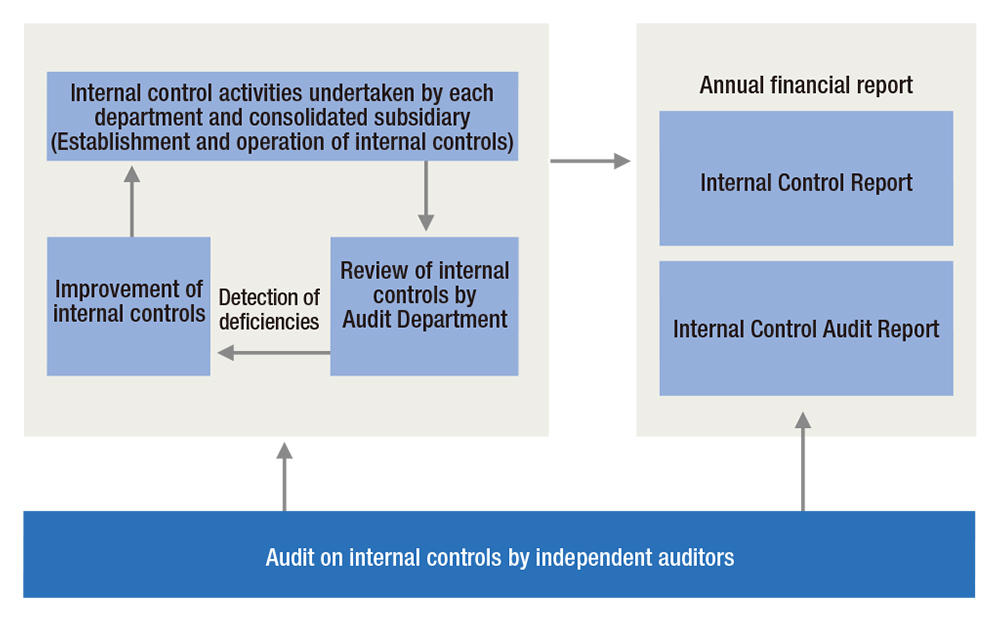
Furthermore, based on the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law (so-called Japanese Sarbanes-Oxley Act (J-SOX)), we have established an internal control system to maintain the reliability of financial reporting. The system’s status and progress are evaluated by the Internal Audit Office and audited by independent auditors. We determine which TICO Group companies fall within the scope of J-SOX based on the degree of impact on the reliability of financial reporting. We determined that our internal controls over financial reporting as of the end of FY2025 were effective, and accordingly, submitted an Internal Control Report in June 2025. The report was reviewed by independent auditors and judged fair in their Internal Control Audit Report. As part of our internal controls, we also have an audit system to ensure appropriate, ethical, and integrity-driven business operations. With the Internal Audit Office taking the lead, we periodically and systematically perform various audits, including audits based on self-assessment questionnaires (self-audits), business audits, theme audits, and J-SOX assessments, at a scheduled interval of three to five years. Through these audits, we seek to strengthen our Group-wide risk management and compliance. These audits are conducted on all departments within TICO and our major subsidiaries around the world and help us detect risks early and prevent them from materializing.
Internal Control Assessment System
(Based on J-SOX)
Compliance
Basic Perspective
We believe that compliance means both adhering to laws and regulations as well as ethics and social norms. As such, it is vital to promote compliance throughout the Toyota Industries Group under the leadership of top management.
As part of these efforts, we established the Compliance Committee in July 2024. Chaired by the Global Chief Compliance Officer (GCCO), the committee is composed of management executives, including the Chairman and President. Its purpose is to oversee the consolidated Group’s compliance program and ensure its effective and sustained implementation on a global scale.
In addition, as one of our key initiatives, we are undertaking the global transformation of our compliance program to ensure that employees conduct business with integrity based on measures to prevent recurrence of the engine certification issue in Japan that we announced in March 2023. Specifically, we are implementing timely and appropriate measures such as developing and implementing compliance-related rules applicable across the entire Group; holding compliance training; gathering information on legal trends including new laws and revisions as well as on sample cases at other companies; and identifying and assessing compliance risks.
We are also working to foster a culture in which employees feel comfortable raising questions or concerns. For matters requiring investigation, we ensure that prompt and appropriate investigations and corrective actions are carried out. Furthermore, we have established a framework whereby serious issues—such as violations of certification regulations or antitrust laws, as well as bribery and corruption—are promptly reported to the Board of Directors through the GCCO and the Compliance Committee.

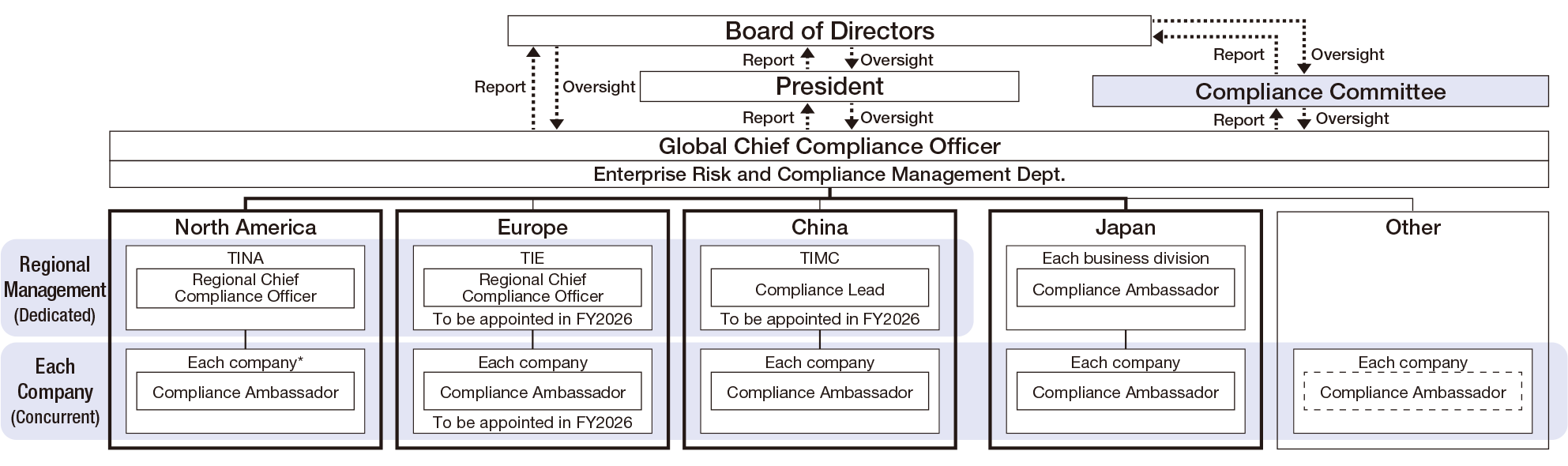
Establishing a Global Compliance Organization
TICO’s global compliance promotion is led by the Enterprise Risk and Compliance Management Department, established as part of our broader compliance program transformation. This department is responsible for implementing, monitoring, and continuously enhancing the compliance program. In Japan, Compliance Ambassadors have been appointed within each business division and domestic subsidiary. Under the direction of the Enterprise Risk and Compliance Management Department, these Ambassadors work to raise compliance awareness and support the execution of related activities. Additionally, Compliance Leads have been assigned within the Enterprise Risk and Compliance Management Department for the TOYOTA Material Handling Company, Engine Division, and Compressor Division. Taking into account the engine certification issue and each division’s risk profile, these Leads guide and support compliance efforts across both the divisions and their respective domestic subsidiaries.
Overseas, a Regional Chief Compliance Officer (RCCO) was appointed at the subsidiaries overseeing our Group’s operations in North America in May 2024 and in Europe in August 2025 to promote, manage, and oversee the compliance program across the region. In China, Compliance Ambassadors were appointed at each subsidiary in February 2025, as well as Compliance Lead in July 2025 to oversee compliance activities for all local subsidiaries. We also plan to designate Compliance Leads and Ambassadors in other regions based on their respective risk profiles.

Responsibilities of Officers
We have added compliance-related provisions to the prohibitions outlined in the regulations for senior executive officers and executive officers. We have also clearly stated the potential impact on remuneration in the event of violations. These measures are intended to promote the prevention, detection, and response to business activities that violate laws, regulations, and company policies.
Formulating Ethics & Compliance Declaration and Toyota Industries Group Code of Conduct, and Strengthening of Training and Awareness Activities

In July 2024, we formulated the Ethics & Compliance Declaration affirming our commitment to doing the right things in the right ways. We also revised the former Code of Conduct and established the Toyota Industries Group Code of Conduct, which sets ethical and compliance standards applicable to executives and employees of TICO and its consolidated subsidiaries.
At TICO and its Group companies in the United States, the Group Code of Conduct was distributed to all executives and employees, followed by training sessions held from November 2024 through January 2025. We will continue to conduct annual awareness activities going forward. In other regions, similar education efforts will begin in FY2026.
In addition, based on the findings and reflections from the Special Investigation Committee’s report on the engine certification issue—specifically the criticism that management was informed of the problem but failed to take corrective action—we launched new compliance training for managers in February 2024. This ongoing practical training aims to raise compliance awareness among managers, promote workplaces where employees feel comfortable raising concerns, prohibit unfair treatment of whistleblowers, and guide appropriate responses when receiving compliancerelated consultations.
As another effort, we have created and disseminated e-learning materials on 49 topics and compliance mini quizzes on 48 topics in order to cultivate a deeper understanding of compliance among employees of TICO and our consolidated subsidiaries in Japan and to create an environment in which employees learn about compliance on their own.
Throughout the year, top management repeatedly communicates the importance of compliance itself, as well as the importance of reporting and consulting on compliance violations and the prohibition of unfair treatment of whistleblowers. Furthermore, to promote compliance awareness, the GCCO shares insights internally through a column titled “Window to Compliance.”
Execution rate of the Code of Conduct enlightenment and educational activities by Toyota Industries and consolidated subsidiaries in and outside Japan: 100%

Compliance Proposal Desk
In February 2025, we established a Compliance Proposal Desk to internally collect improvement suggestions, observations, and ideas related to compliance. To raise compliance awareness and encourage active participation, we also plan to recognize and reward outstanding suggestions that will lead to actual improvements.
Efforts on Export Control for Security Trade
For overseas exports, we have established a system that, in accordance with Company-wide rules, reviews each export transaction to determine whether the items fall under export control regulations and whether the intended use at the destination is related to military uses.
We ensure strict compliance with these laws by holding annual employee training to raise awareness and by monitoring the operational status through audits.
These measures are deployed across Group companies in and outside Japan to ensure a global response.
Efforts for Prevention of Bribery
To prohibit and prevent bribery, in 2014 Toyota Industries formulated the Global Guidelines for Bribery Prevention (or individual rules in countries high on the Corruption Perceptions Index in accordance with their respective, applicable laws) and has been conducting activities to familiarize employees with them in each country and region.
In March 2023, we formulated the Toyota Industries Group Anti-Bribery Policy to clarify our stance both within and outside the Toyota Industries Group. We have positioned the policy above our Global Guidelines for Bribery Prevention and have been working to communicate and thoroughly implement the policy in each region and country.
 Toyota Industries Group Anti-Bribery Policy PDF [220.3KB / 1pages]
Toyota Industries Group Anti-Bribery Policy PDF [220.3KB / 1pages]
Efforts for Ensuring Compliance with Antitrust Laws
As for antitrust laws, we operate a system to conduct a check and review before and after employees of Toyota Industries contact competitors and have been cultivating awareness among employees for not acting in a manner that may possibly constitute a violation of antitrust laws. Moreover, we have designated a particular month as “Antitrust Law Compliance Month” since fiscal 2016 to carry out enlightenment activities at relevant departments for clarifying our relationships with competitors and ensuring fair transactions with business partners (e.g., the need to hold sincere dialogue with business partners to deal with changes in the business environment caused by rises in various costs).
Consolidated subsidiaries in and outside Japan have also been working to educate and raise awareness of employees to preventing violations of antitrust laws, such as forming cartels, in accordance with local laws and regulations.
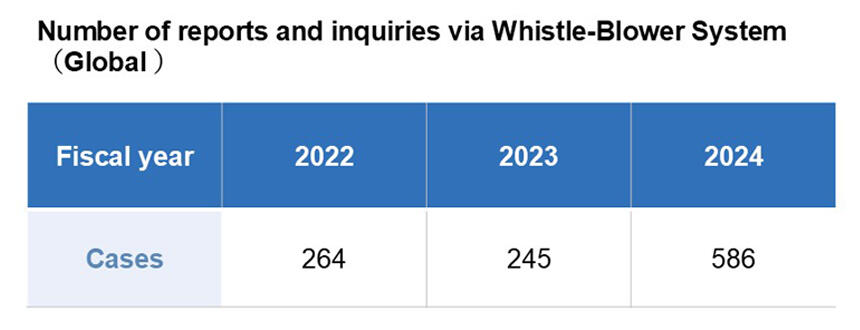
Early Detection and Prevention of Issues via Whistleblower System
The TICO Group operates a whistleblower system (helpline) and a reporting and consultation desk for business partners in each region, through which employees, business partners, and others can anonymously report and seek consultation on compliance-related matters at their convenience. We accept reports and inquiries through law firms, dedicated external websites, and other means. In FY2025, we received 586 reports and inquiries from within TICO and from its consolidated subsidiaries in and outside Japan on matters such as labor management and work environment issues. All cases received are handled confidentially by the department in charge of the whistleblower system and other relevant parties in accordance with company rules. Appropriate investigations are conducted to ascertain the facts, and necessary measures are taken. Additionally, any adverse treatment due to reporting or consultation is strictly prohibited.
Going forward, we will continue to promote awareness and improvement of the whistleblower system and foster an environment where employees and others feel comfortable speaking up. Through these efforts, we aim to facilitate early discovery and prevention of issues and strive to become a “company on which society places greater trust.”
Compliance Awareness Survey
The compliance awareness survey, which was issued once every three years, will be conducted annually from FY2026 onward to assess the effectiveness of the compliance program and facilitate its continuous improvement.
Tax Governance
Basic Perspective
The TICO Group regards the most important managerial task as earning trust broadly from society and enhancing its corporate value on a stable, long-term basis in accordance with our Basic Philosophy and by earnestly fulfilling our social responsibilities. We strive to contribute to society and maintain and enhance corporate value by complying with the applicable tax laws and regulations of each country and region, where we undertake business activities, as well as by paying the appropriate level of taxes.
Tax Policy
Under the basic perspective, Toyota Industries has formulated the Toyota Industries Group Tax Policy.
The Toyota Industries Group will educate its employees as necessary through tax and accounting training and e-learning programs so that we are able to pay the appropriate level of taxes and take the proper tax measures in accordance with the Toyota Industries Group Code of Conduct.
 Toyota Industries Group Tax Policy PDF [376.4KB / 1pages]
Toyota Industries Group Tax Policy PDF [376.4KB / 1pages]
Risk Management
Basic Perspective
Based on the Basic Policies for the Establishment of an Internal Control System in compliance with the Companies Act, TICO is working to strengthen regulations and a structure to promote risk management. We regard the following aspects as the basics of risk management and implement initiatives accordingly.
(1) Incorporating measures to prevent and reduce potential risks into daily routines and following up on the progress of implementation
(2) Ensuring quick and precise actions to minimize the impact on business and society when a risk becomes apparent
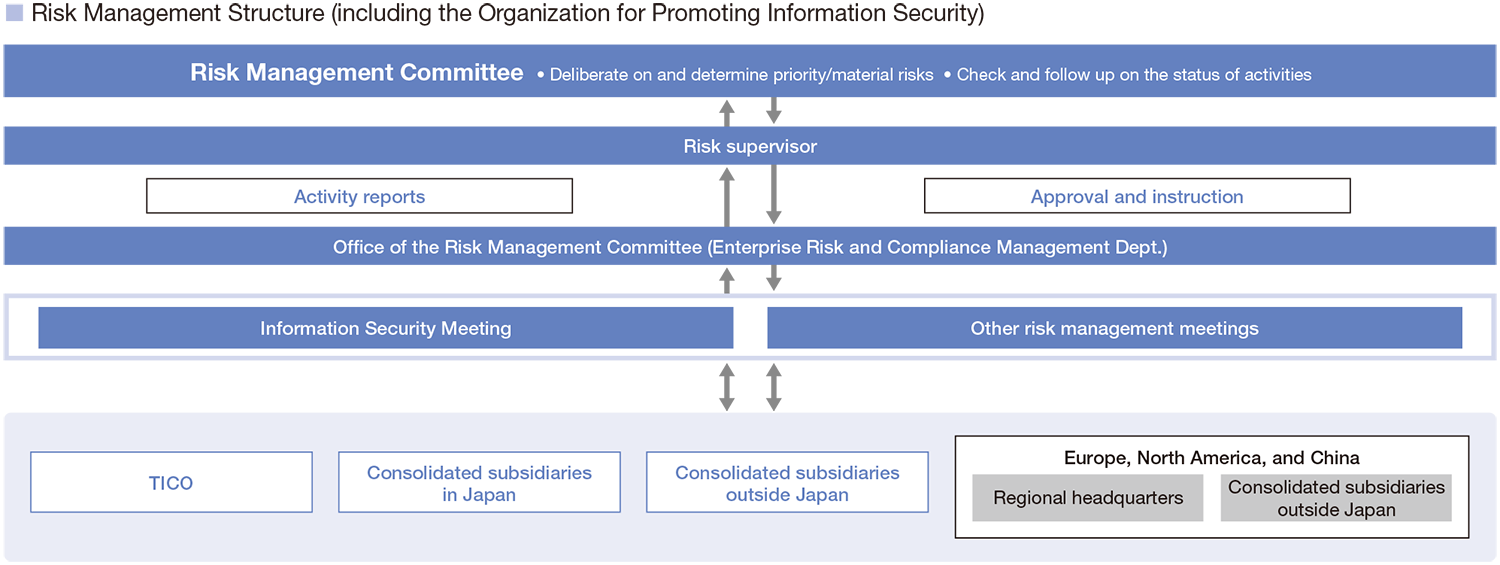
Implementation Structure
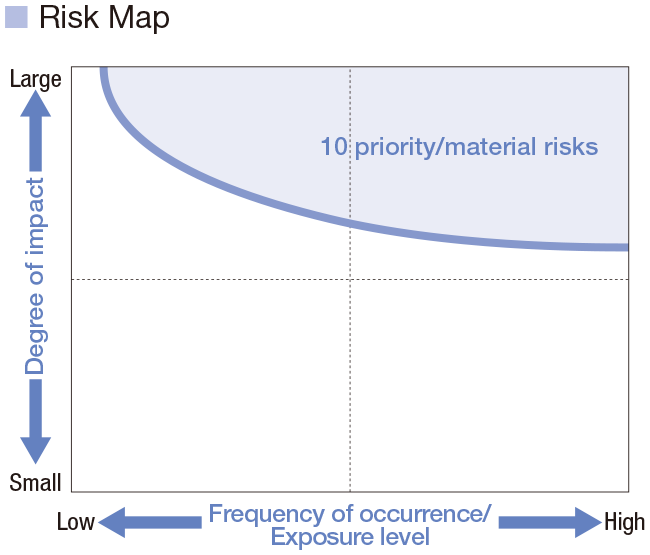
Business divisions and other departments at the Head Office develop and promote annual action policies that integrate measures to prevent and control risks related to quality, safety, the environment, personnel, export transactions, disasters and information security. Progress is assessed and followed up by each functional management entity. Previously, the CSR Committee was responsible for risk management of the entire Company. However, in order to further strengthen our risk management efforts, we newly established the Risk Management Committee, chaired by the risk supervisor (executive in charge of enterprise risk and compliance management), on April 1, 2024.
The Risk Management Committee promotes activities to identify priority/material risks from among risks concerning Toyota Industries as a whole and make sure to implement measures at each functional management entity as well as measures to counter emerging risks spanning multiple functions.
At the same time, functional departments at the Head Office such as those responsible for safety, quality and the environment formulate rules and regulations and create manuals from a Group-wide perspective, encompassing consolidated subsidiaries. By confirming and following up on the progress through operational audits and workplace inspections, they provide support for raising the level of risk management, including the ability to respond to the identified priority/material risks, at each business division and consolidated subsidiary.
We have also formulated the Risk Response Manual, which defines basic rules for risk management activities under normal circumstances and for our initial response to an emergency when a risk becomes evident. The aim is to ensure quick reporting to top management, perform an accurate assessment of the impact on society and business activities and minimize damage through appropriate actions. The content of the manual is reviewed and revised as deemed necessary in response to changes in businesses and the surrounding environment.
Information Security
Basic Perspective
Under the Basic Philosophy and the Sustainability Policy, we recognize that the personal information of customers, employees, and business partners as well as information concerning our technologies, sales activities, facilities, and products are assets that need to be protected. Accordingly, with the aim of safeguarding our information assets and strengthening their management, we have formulated the Basic Policies for Information Security.
Basic Policies for Information Security
- (1) Legal compliance
- We comply with laws and regulations related to information security while fostering awareness of them among employees.
- (2) Maintaining a stable business foundation
- We safeguard and manage information assets appropriately, carry out information security-related education and enlightenment activities on an ongoing basis and seek to maintain a stable business foundation.
- (3) Providing safe products and services
- We provide safe products and services to customers and society by implementing information security measures in our business activities, including the development, design and manufacture of products and services.
- (4) Information security management
- We build a governance structure to enforce and manage information security and continue to promote and refine the structure.
Implementation Structure
Toyota Industries has set up the Risk Management Committee (led by a risk supervisor*1) as a subordinate organization to the Information Security Meeting (chaired by an executive in charge of promoting information technology (IT) and digitalization) to reduce information security risks.
To thoroughly implement the initiatives adopted by the Information Security Meeting, we appoint Confidentiality Management Champions*2 and Confidentiality Management Supporters*3 at each department of Toyota Industries.
For consolidated subsidiaries around the world, we regularly hold meetings of IT managers in each region to share information on security incidents and countermeasures both in and outside the Toyota Industries Group and to disseminate relevant policies. Through these and other measures, we are increasing the levels of security and security awareness throughout the Group.
*1: Executive in charge of enterprise risk and compliance management
*2: Head of each department
*3: A person within the department, appointed by the head
Information Security Management
Information Security Monitoring and Incident Response
To ensure the early detection of and prompt action against cyberattacks, we have in place systems to monitor the security of PCs and all other terminals used within the Toyota Industries Group and to respond to incidents 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. We also share threat information with our consolidated subsidiaries in and outside Japan to swiftly alert each company.
Number of serious incidents occurred: 0
Strengthening Information Security Governance within the Group
In accordance with the All Toyota Security Guidelines (ATSG)*4, we annually inspect the implementation status of information security at Toyota Industries and our consolidated subsidiaries and affiliates around the world in order to maintain and improve the level of information security on a continuous basis.
We are also promoting the achievement of a uniform, more sophisticated level of security in all Group companies by sharing information on related initiatives through liaison meetings of affiliated companies in Japan and the TICO Group Cyber Security Summit meetings. We also visit individual Group companies to support their efforts.
*4: Security guidelines of the Toyota Group, which conform to the Cyber Security Framework of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST CSF) and ISO 27000 series of standards for information security management systems
Reinforcing Efforts to Enhance Information Security Awareness
With the aim of establishing a structure under which each department voluntarily promotes information security according to the risks associated with its operational characteristics, we are working to raise the level of security awareness among all employees through grade-based education and training.
Primary Activity Examples

| Activities in FY2025 |
|---|
|
Activities Related to Intellectual Properties
Basic Perspective
One tenet of the Toyoda Precepts, which encapsulates the spirit of our founder, Sakichi Toyoda, states, “Always be studious and creative, striving to stay ahead of the times.” Carrying on this spirit, we actively engage in research and innovation. We leverage the resulting intellectual property rights, including inventions and know-how, to support the strategies of each business. Furthermore, by securing intellectual property rights in and outside Japan and preventing infringement, we strive to enhance corporate value through the effective management of intellectual property.
Intellectual Property Activities Aligned with the Technology Roadmap
Technological development is becoming increasingly important to achieving our 2030 Vision. As such, we review what intellectual property is necessary for our business based on the technology roadmap formulated by each technology development department. We also formulate strategies to establish competitive advantages by monitoring competitors’ business strategies.
Our business domains are expanding into new technology fields such as IoT, AI, autonomous driving, and carbon neutrality. We maintain a keen awareness of these emerging technologies and strengthen our competitiveness by actively creating intellectual property and intangible assets, including know-how and software, in addition to conventional intellectual property rights. To support this, we have established a dedicated IP landscape team that explores industry trends and prospects. This team timely disseminates intellectual property information that accelerates development and supports our business efforts, ensuring we continue to contribute to society.
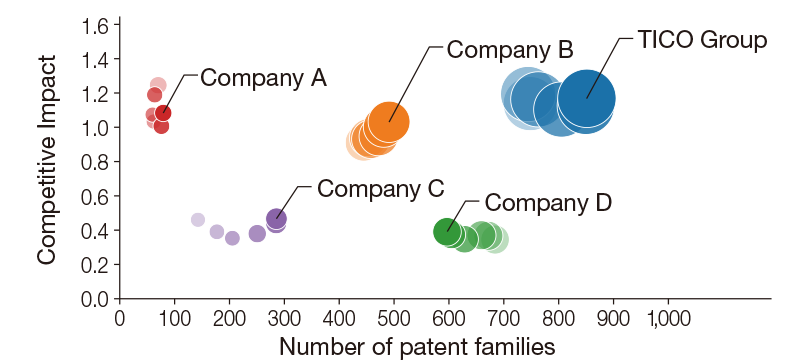
Visualization of Patent Asset Value
We utilize LexisNexis® PatentSight+, a tool developed by U.S.-based LexisNexis, as an objective indicator for analyzing and evaluating the value of our patent assets. Based on the technology roadmap of the Materials Handling Equipment Division, which emphasizes the keywords “automation and labor-saving,” “carbon neutrality,” and “safety and comfort,” we identify the technologies we should possess and build a focused patent portfolio in key markets of Japan, the U.S., and Europe, where both our subsidiaries and competitors operate. In doing so, we maintain a competitive advantage in both the quantity and quality of our patents.
![[Reference guideline] Intellectual Property and Intangible Assets Governance Guidelines](../item/img_governance_25_11_1.png)
(Materials Handling Equipment)