Toyota Industries Corporation Develops a New, More Compact On-Board Electricity Supply Unit for BEVs
- New Control Technologies Enable Support for the Power Transmission Methods Used in Various Countries and a Wide Range of Models -
Toyota Industries Corporation ("Toyota Industries") has developed a new on-board electricity supply unit (ESU) that provides charging and power supply functions for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Countries and regions use various different power transmission methods as a result of their respective electrical situations. Toyota Industries has created a lineup of products around the world that now support those diverse power transmissions while at the same time providing high power output. These products can be used in a wide range of vehicles, from compact cars to large vehicles. The newly developed ESU has even higher output and better power supply support, and it can be used in even more models thanks to its compact size and low profile. It is being used in the all-new bZ4X, which was launched by Toyota Motor Corporation ("Toyota Motors") on October 9.
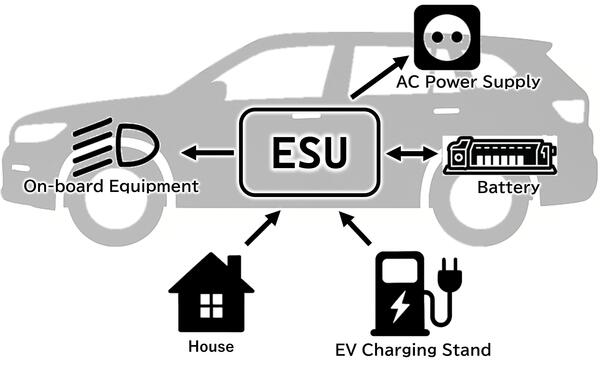
The ESU is a critical power electronics component that enables BEVs to use electrical power efficiently. It integrates standard charging and rapid charging functions, power supply functions, DC-DC conversion (voltage conversion) functions, and power distribution functions. It is involved in charging using an EV charging stand, supplying power to home appliances, and powering electrical devices within vehicles.
Toyota Industries has supplied compact, lightweight units for BEVs that combine chargers with DC-DC converters. In developing the entire ESU, Toyota Industries has integrated a DC relay that supports high voltages and high currents for use in rapid charging, a power distribution unit (PDU) for distributing power, and power supply functions. This ESU is the first in the world*1 to use Toyota Industries' proprietary current control technologies. This makes it possible for a single circuit to control different power transmission methods, which vary depending on the country or region, such as single-phase power, the main type of power used in Japan and North America, or the three-phase power primarily used in Europe. It therefore supports charging from household power supplies in various countries.
It also has a high output, with simultaneous support for six output variations, from 7 kW to 22 kW. This makes it possible to use in diverse vehicle models in different classes, which contributes to lower costs thanks to the benefits of mass production. To meet the needs of users in major markets, it also supports the NACS charging standard, which is the most commonly used standard in North America.
Not only does it add these functions, but it also features an optimized structure that makes it 26% more compact*2 than previous devices.
Since the 1990s, Toyota Industries has been developing and producing on-board chargers, DC-DC converters, AC inverters, and other devices for use in Toyota hybrid electric vehicles and other electrified vehicles. Over the years, it has polished its power electronics technologies. The BEV market is growing due to factors such as moves towards realizing carbon neutrality by 2050, automated driving,
and software-defined vehicles (SDVs) whose functionality can be improved using software. Power electronics technologies are becoming more and more important.
Toyota Industries remains committed to developing compact, lightweight and highly efficient power electronics technologies while continuing to provide car electronics products, including the newly unveiled ESU, to support the wider use of BEVs.
| *1 | The first in the world to apply these technologies to chargers, according to research by Toyota Industries |
| *2 | Improvements in output performance make the unit 26% more compact in terms of volume per unit of output (when compared to single-phase 11 kW units) |